IPv6 Support in CloudStack
CloudStack has limited IPv6 support. It supports IPv6 for shared and isolated networks. It also supports IPv6 for VPC Network Tiers.
Isolated network and VPC Network Tier
Note
The IPv6 support for isolated networks and VPC Network Tiers is available from version 4.17.0.
The IPv6 isolated networks and VPC Network Tiers only supports Static routing, i.e, the administrator will need to add upstream routes for routing to work inside the networks.
IPv6 only isolated networks and VPC Network Tiers are not supported currently. Public network for IPv6 supported isolated networks and VPC Network Tiers must be on the same VLAN for both IPv4 and IPv6.
Guest Instances in an isolated network or VPC Network Tier can obtain both IPv4 and IPv6 IP addresses by using a supported network offering and appropriate configurations for IPv6 support by the administrator. Both VR for such networks and the Guest Instances using these networks obtain a SLAAC based IPv6 address. While VR is assigned an IPv6 address from the public IPv6 range, Guest Instances get their IPv6 addresses from the IPv6 subnet assigned to the network.
Here’s the sequence of events when IPv6 is used:
The administrator sets global configuration -
ipv6.offering.enabledto true.The administrator adds a public IPv6 range in an advanced zone.
The administrator adds an IPv6 prefix for guest traffic type for the zone.
The administrator creates a network or VPC offering with IPv4 + IPv6 (Dual stack) support.
The user deploys an isolated network with the IPv6 supported network offering. For VPC, user creates a VPC with IPv6 supported VPC offering and then deploys a Network Tier with IPv6 supported network offering.
CloudStack assigns a SLAAC based public IPv6 address to the network from the public IPv6 range of the zone. It also assigns an IPv6 subnet to the network from the guest IPv6 prefix for the zone. See SLAACfor more information.
The user deploys a Guest Instance in the network. The Instance is assigned a SLAAC based IPv6 address from the guest IPv6 subnet of the network.
Prerequisites and Guidelines
Consider the following:
CIDR size for the public IPv6 range for a zone must be 64.
CIDR size for the guest IPv6 prefix for the zone must be lesser than 64. Each guest network is assigned a subnet from this prefix with CIDR size 64 therefore only as many IPv6 supporting guest networks can be deployed from the guest prefix as the number of subnets with CIDR size 64.
Currently, a guest network cannot be IPv6 only and it can only be either IPv4 only or Dual Stack (both IPv4 + IPv6).
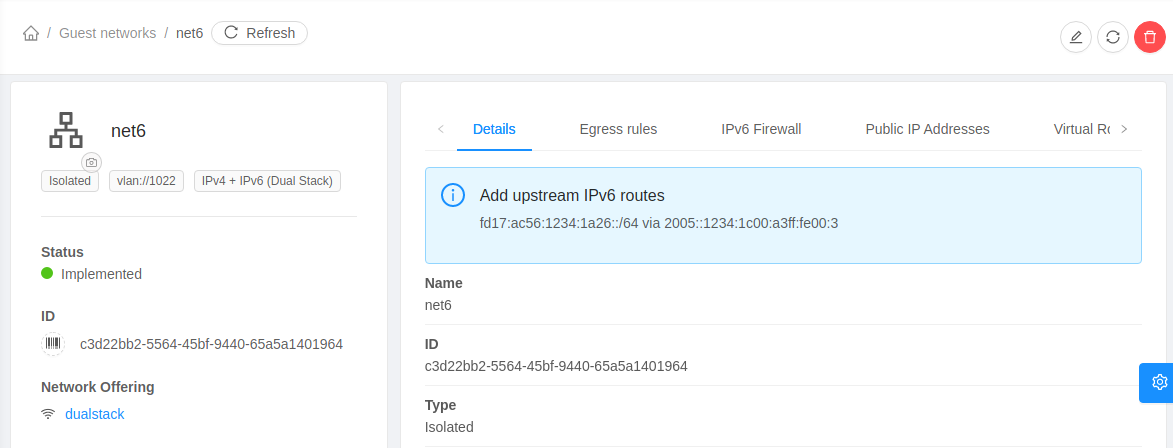
Once a public IPv6 address and guest subnet are assigned to the network or the network is successfully, the operator must update routing in the upstream router. For this, CloudStack returns the gateway and subnet for the network with listNetworks API response.
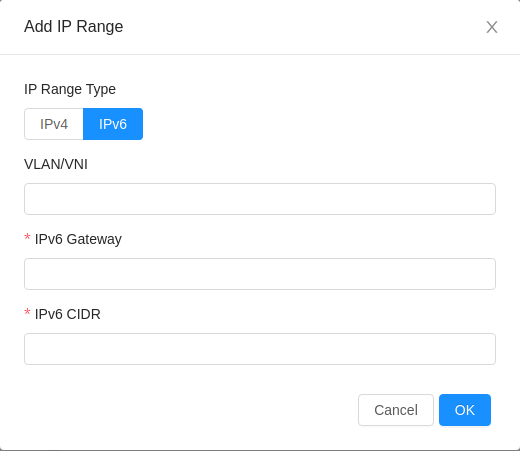
Adding a Public IPv6 Range
The administrator can use both UI and API to add a public IPv6 range. UI is the preferable option. Option to add a new public IPv6 range in the UI can be found in Infrastructure > Zones > Zone details > Physical Network tab > Physical network details > Traffic Types tab > Public > Add IP range. In the Add IP range form, IPv6 can be selected as the IP Range Type. IPv6 Gateway and CIDR must be provided and optionally a VLAN/VNI can be provided.
Alternatively, createVlanIpRange API can be used to add a new public IPv6 range.
Note
The public IPv6 address range or CIDR must be added with same VLAN as that of public IPv4 address range.
As SLAAC based public IPv6 addresses will be assigned to the networks therefore public IPv6 range must be added without specifying start and end IP addresses.
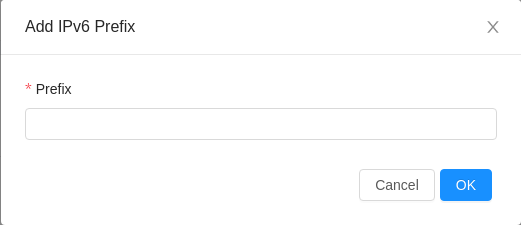
Adding Guest IPv6 Prefix
Again, both UI and API to add a guest IPv6 prefix. UI is the preferable option. Option to add a new public Ipv6 range in the UI can be found in Infrastructure > Zones > Zone details > Physical Network tab > Physical network details > Traffic Types tab > Guest > Add IPv6 prefix. In the Add IPv6 prefix form, an IPv6 prefix with CIDR size lesser than 64 must be provided.
Alternatively, createGuestNetworkIpv6Prefix API can be used to add a new guest IPv6 prefix.
Adding Network or VPC Offering with IPv6 Support
To create an IPv6 supported network or VPC offering, global configuration - ipv6.offering.enabled must be set to true.
- With 4.17.0, a new parameter -
internetprotocolhas been added to: the
createNetworkOfferingAPI which can be used to create a network offering with IPv6 support by using the value dualstack.the
createVPCOfferingAPI which can be used to create a VPC offering with IPv6 support by using the value dualstack.
Corresponding option has also been provided in the UI form creating network/VPC offering:
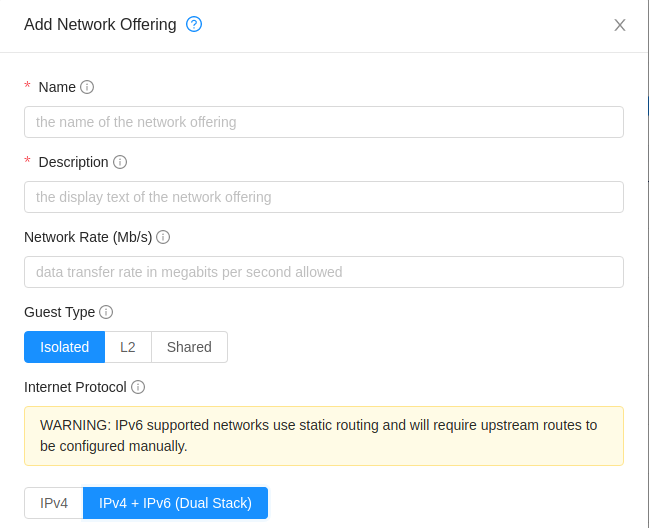
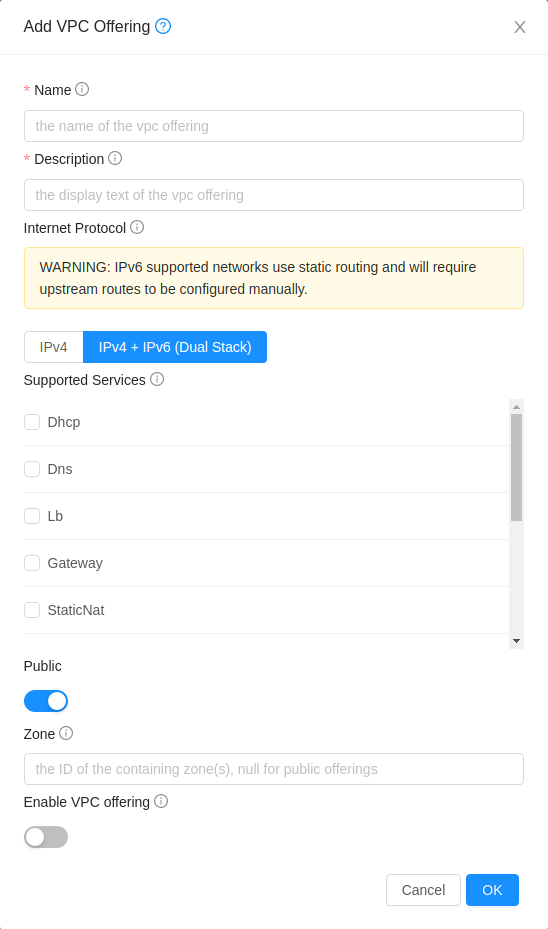
Adding Upstream Route
Currently, CloudStack supports IPv6 isolated networks and VPC Network Tiers only with static routes and therefore the administrator needs to add upstream IPv6 routes once a network is successfully deployed. To facilitate the automation, CloudStack Event Notification can be used. CloudStack will generate appropriate events on network creation or deletion and while assigning or releasing a public IPv6 address for a network. Based on the events the corresponding network can be queried for the IPv6 routes that it needs configured in upstream network. Upstream IPv6 routes required by an IPv6 supported isolated network or VPC Network Tier are also shown in the UI in the network details.
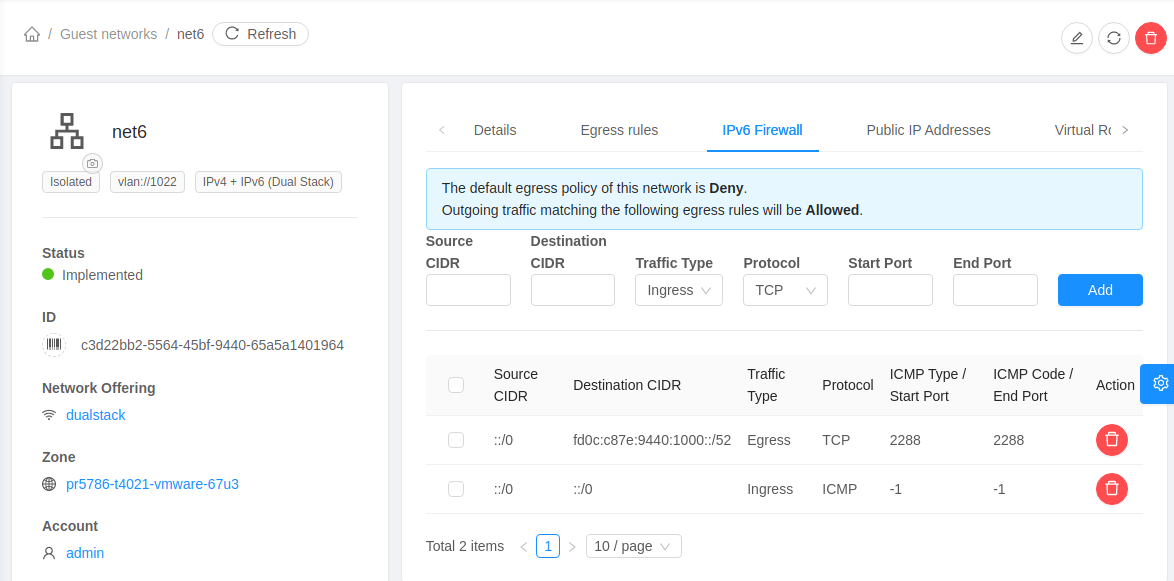
IPv6 Firewall
For using and managing firewall rules with an IPv6 supported isolated network, CloudStack provides following APIs:
listIpv6FirewallRules- To list existing IPv6 firewall rules for a network.createIpv6FirewallRule- To create a new IPv6 firewall rules for a network.updateIpv6FirewallRule- To update an existing IPv6 firewall rules for a network.deleteIpv6FirewallRule- To delete an existing IPv6 firewall rules for a network.
These operations are also available using UI in the network details view of an IPv6 supported network.
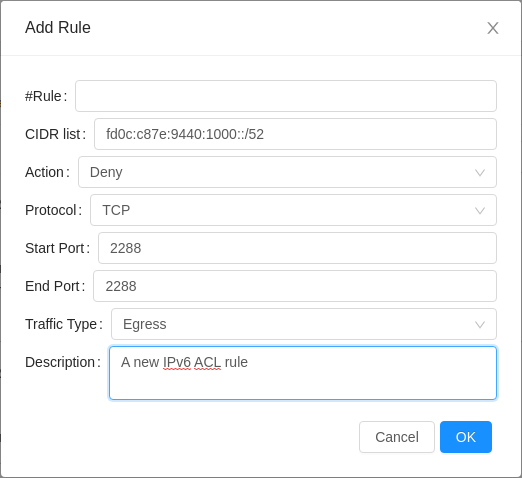
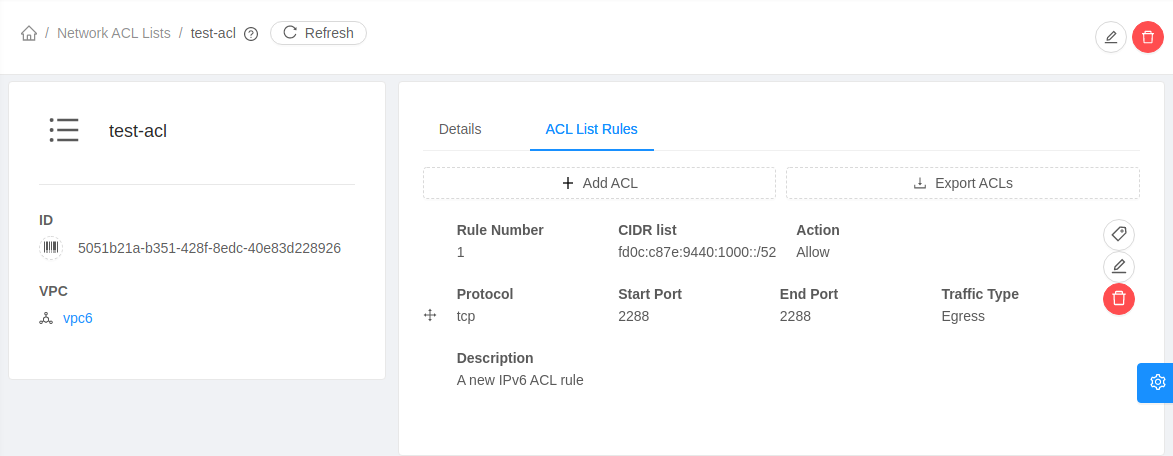
IPv6 ACL
IPv6 ACL rules for an IPv6 supported VPC Network Tier can be managed using Network ACL lists for the VPC. IPv6 CIDRs can be specified while adding or updating an ACL rule.