CloudStack Kubernetes Service
The Kubernetes Service plugin adds Kubernetes integration to CloudStack. The plugin is disabled by default and an admin can enable it using a Global Setting. It enables users to run containerized services using Kubernetes clusters.
With CoreOS having reached EOL, from 4.16 on the Kubernetes Service Plugin will use the existing SystemVM Template by default for deploying kubernetes clusters. For installation of Kubernetes binaries on the cluster nodes, a binaries ISO is used for each Kubernetes version to be made available via CloudStack. This allows faster, offline installation of Kubernetes binaries and docker images along with support for adding multiple versions of Kubernetes for upgrades and running different clusters.
Note
From version 4.21.0, users can choose different templates and service offerings for different types of nodes (worker, control, etcd nodes) for deploying Kubernetes clusters. The templates must be previously registered selecting the ‘For CKS’ option. See Flexible Kubernetes Clusters.
For deployment and setup of Kubernetes on cluster nodes, the plugin uses the Kubernetes tool, ‘kubeadm’. kubeadm is the command-line tool for easily provisioning a secure Kubernetes cluster on top of physical or cloud servers or Instances. Under the hood, control node(s) of the cluster starts a Kubernetes cluster using kubeadm init command with a custom token, and worker nodes join this Kubernetes cluster using kubeadm join command with the same token. More about kubeadm here: https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/setup-tools/kubeadm/kubeadm/. Weave Net CNI provider plugin is used for cluster networking. More about Weave Net provide plugin here: https://www.weave.works/docs/net/latest/kubernetes/kube-addon/.
To access the Kubernetes dashboard securely, the plugin provides access to kubeconfig file data which uses the Kubernetes tool kubectl to run a local proxy and thereby access the dashboard. More about kubectl here: https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/
The service allows creation of Kubernetes clusters using the UI or API. Both UI and API provide the ability to list, delete, scale, upgrade, stop and start these clusters.
From ACS 4.19 onwards, you can also create ExternalManaged kubernetes clusters using the API. This helps provide a centralized view of kubernetes clusters managed by other providers.
Enabling the Kubernetes Service
The Kubernetes Service plugin is disabled by default. To enable it, go to Global Settings and set the following global configuration to true:
cloud.kubernetes.service.enabled
Restart the Management Server to enable the set configuration values.
# service cloudstack-management restart
Once the Kubernetes service is running the new APIs will become accessible and the UI will show the Kubernetes tab under the Compute section.
NOTE: From ACS 4.16 onwards, if a CKS cluster is to be deployed on VMware, the ‘vmware.create.full.clone’ configuration parameter will need to be set to true, so as to allow resizing of root volumes of the cluster nodes.
Kubernetes Supported Versions
The Kubernetes service provides the functionality to manage multiple supported Kubernetes versions. Management can be via both UI and API. A supported version corresponds to a specific Kubernetes version for which an ISO has been uploaded. Pre-built, community ISOs for different Kubernetes versions are available at:
A script is provided (see below) to add other Kubernetes versions. Once an ISO is created for a Kubernetes version it can be added in the service and other CRUD operations can be performed using both the UI and API. Using a pre-packaged ISO containing required binaries and docker images allows faster provisioning on the node Instances of a Kubernetes cluster. Complete offline provisioning of the Kubernetes cluster is not supported at present as the kubeadm init command needs active Internet access.
A script named create-kubernetes-binaries-iso.sh has been provided in the cloudstack-common package for creating a new setup ISO with the desired version of Kubernetes binaries and corresponding docker images.
Eg: To generate the latest kubernetes iso
1.27.2, kubernetes version, see https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/releases
1.3.0, CNI version, see https://github.com/containernetworking/plugins/releases
1.27.0, cri-tools version, see https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/cri-tools/releases
1.11, weave addon for kubernetes, see https://github.com/weaveworks/weave/tree/master/prog/weave-kube
2.7.0, kubernetes dashboard version, see https://github.com/kubernetes/dashboard/release
Usage:
# ./create-kubernetes-binaries-iso.sh OUTPUT_PATH KUBERNETES_VERSION CNI_VERSION CRICTL_VERSION WEAVENET_NETWORK_YAML_CONFIG DASHBOARD_YAML_CONFIG [OPTIONAL_OUTPUT_FILENAME] [OPTIONAL_ETCD_VERSION]
Eg:
# ./create-kubernetes-binaries-iso.sh ./ 1.27.2 1.3.0 1.27.0 https://raw.githubusercontent.com/weaveworks/weave/master/prog/weave-kube/weave-daemonset-k8s-1.11.yaml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.7.0/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml setup-v1.27.2
NOTE: From ACS 4.16 onwards, Kubernetes versions >= 1.20.x are only supported (https://endoflife.date/kubernetes).
NOTE: From ACS 4.21 onwards, it is possible to specify the version for etcd binaries in the create-kubernetes-binaries-iso.sh script as an optional parameter - ETCD_VERSION. When the ETCD_VERSION parameter is set, the specified etcd version binaries are downloaded and stored in the Kubernetes ISO.
Example for etcd version 3.5.1:
# ./create-kubernetes-binaries-iso.sh ./ 1.27.2 1.3.0 1.27.0 https://raw.githubusercontent.com/weaveworks/weave/master/prog/weave-kube/weave-daemonset-k8s-1.11.yaml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.7.0/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml setup-v1.27.2 3.5.1
To deploy Kubernetes clusters with Kubernetes ISOs built with a specified etcd version are necessary for creating Kubernetes clusters with separate etcd nodes. See Flexible Kubernetes Clusters.
Working with Kubernetes supported version
Adding supported Kubernetes version
Once the ISO has been built for a desired Kubernetes version, it can be added by the admin in the service for cluster deployment using both the UI and API. The UI provides the following form to add new supported version:
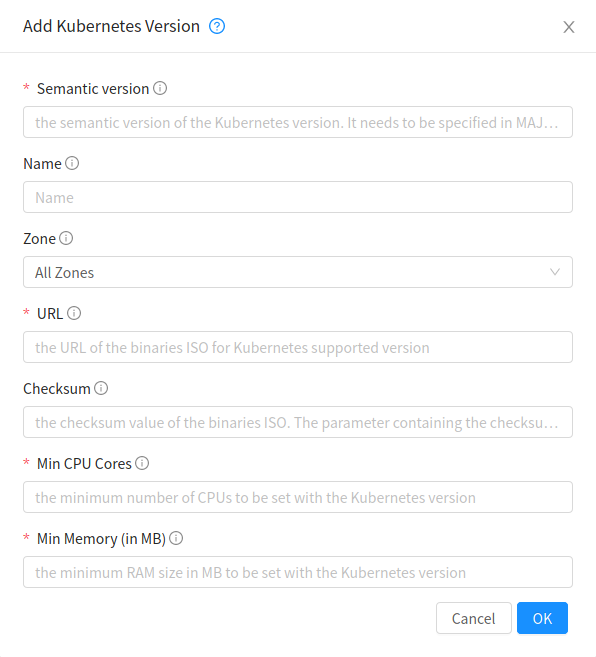
Note
From 4.21.0, it is possible to deploy separate dedicated etcd nodes. This requires the Kubernetes ISO contains the etcd binaries.
addKubernetesSupportedVersion API can be used by an admin to add a new supported version for the service. It takes following input parameters:
name (the name of the Kubernetes supported version) · semanticversion (the semantic version of the Kubernetes release in MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH format. More about semantic versioning here: https://semver.org/ Required)
zoneid (the ID of the zone in which Kubernetes supported version will be available)
url (the URL of the binaries ISO for Kubernetes supported version)
checksum (the checksum value of the binaries ISO)
mincpunumber (the minimum number of CPUs to be set with the Kubernetes supported version)
minmemory (the minimum RAM size in MB to be set with the Kubernetes supported version)
For example:
> add kubernetessupportedversion name=v1.13.2 semanticversion=1.13.2 url=http://172.20.0.1/files/setup-1.13.2.iso zoneid=34d23dd5-5ced-4e8b-9b0a-835a0b8ae2a6 mincpunumber=2 minmemory=2048
{
"kubernetessupportedversion": {
"id": "6668e999-fe6c-4a91-88d8-d10bcf280d02",
"isoid": "78d45e9b-a482-46f4-8cbc-cf7964564b85",
"isoname": "v1.13.2-Kubernetes-Binaries-ISO",
"isostate": "Active",
"semanticversion": "1.13.2",
"name": "v1.13.2",
"supportsha": false,
"zoneid": "34d23dd5-5ced-4e8b-9b0a-835a0b8ae2a6",
"zonename": "KVM-advzone1"
"mincpunumber": 2
"minmemory": 2048
}
}
The minimum Kubernetes version that can be added in the service is 1.11. At present, v1.17 and above might not work due to their incompatibility with weave-net plugin.
Listing supported Kubernetes versions
listKubernetesSupportedVersion API can be used to list existing supported versions. id parameter can be passed as input to list details of a single supported version.
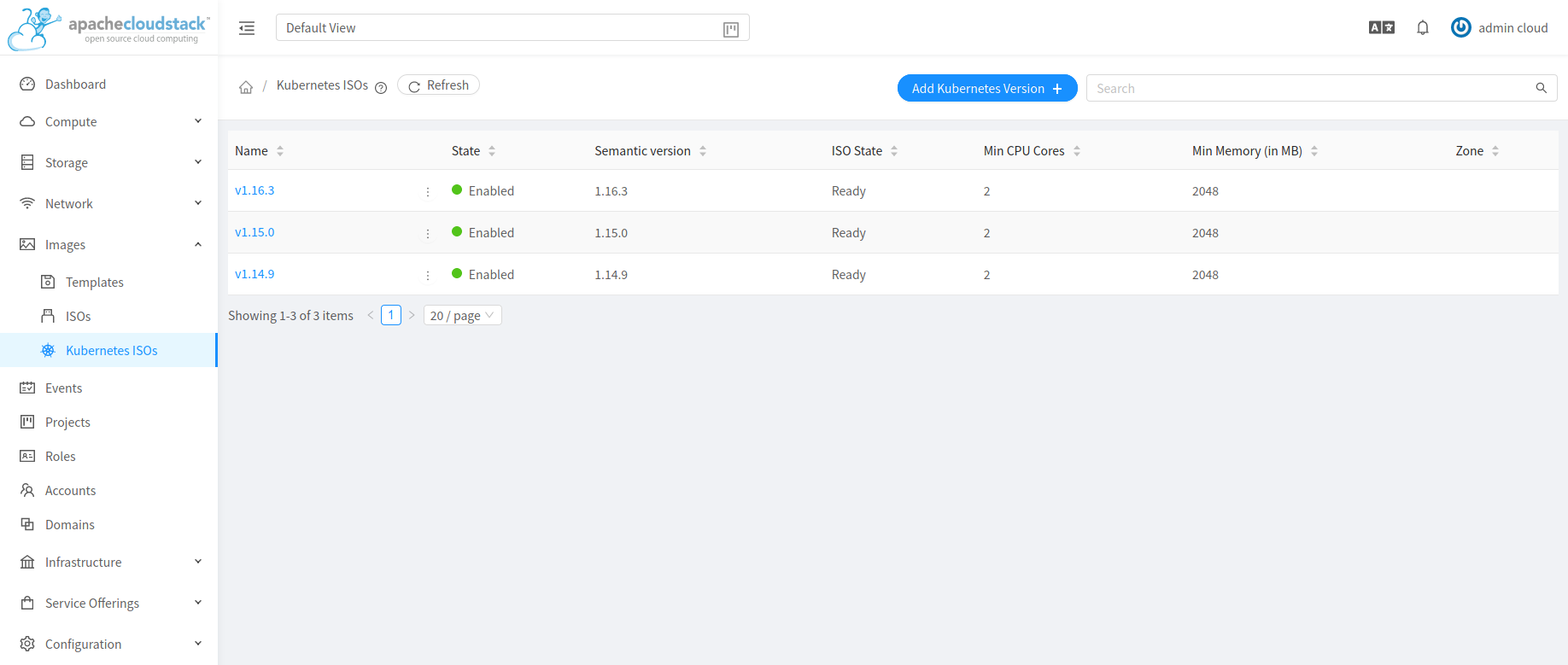
Updating supported Kubernetes version
updateKubernetesSupportedVersion API can be used by admins to update an existing supported version to set their state enabled or disabled. Supported versions with disabled state cannot be used for deploying Kubernetes clusters. It takes following input parameters,
id (the ID of the Kubernetes supported version)
state (the state of the Kubernetes supported version)
Deleting supported Kubernetes version
deleteKubernetesSupportedVersion API has been provided for admins to delete an existing supported version if it is not used by any Kubernetes cluster in the service. id parameter of the API can be used to pass Kubernetes version to be deleted.
Note
addKubernetesSupportedVersion, updateKubernetesSupportedVersion and deleteKubernetesSupportedVersion APIs are available to root admins only
Kubernetes clusters
The Kubernetes service provides the functionality of running and managing Kubernetes clusters. Highly available, scalable Kubernetes clusters can be created to run containerized deployments without having to set up Kubernetes on each container node manually. The service will automatically provision the desired number of Instances as per cluster size using the binaries corresponding to the provided Kubernetes version. Additionally, the service provides the functionality to upgrade and scale clusters. Running clusters can be upgraded to a newer minor or patch Kubernetes version at a time. Running clusters can also be scaled up or down based on the number of worker nodes provided and to the service offering used by each node.
This provides functionality to create Kubernetes clusters for Shared, Isolated and VPC Networks in CloudStack, but such Networks must be accessible to the CloudStack management server for provisioning Instances on the cluster. The default Network offering must be set in the Global Settings for the service to create Kubernetes clusters.
The following Global Setting value must be set to the name of Network Offering to be used for creating a new Network when no Network has been selected while creating a Kubernetes cluster:
cloud.kubernetes.cluster.network.offering
A new Network offering named DefaultNetworkOfferingforKubernetesService has been added since 4.14.0
Note
Multi-control nodes, HA cluster can be created for Kubernetes version 1.16 and above only.
While creating multi-control nodes, HA cluster over a shared Network, an external load-balancer must be manually setup. This load-balancer should have port-forwarding rules for SSH, Kubernetes API server access. Service assumes SSH access to cluster nodes is available from port 2222 to (2222 + cluster node count -1). Similarly, for API access 6443 must be forwarded to control nodes. Over the CloudStack isolated Network these rules are automatically provisioned.
Examples of how to ssh into the Control and Worker nodes
Control node
ssh -i <ssh-private.key > -p 2222 cloud@<Public ip address of Virtual Router>
Worker node
ssh -i <ssh-private.key > -p 2223 cloud@<Public ip address of Virtual Router>
Managing Kubernetes clusters
For Kubernetes cluster management, the service provides create, stop, start, scale, upgrade and delete APIs and similar features in the UI.
Creating a new Kubernetes cluster
New Kubernetes clusters can be created using the API or via the UI. User will be provided with an ‘Add Kubernetes Cluster’ form as shown below,
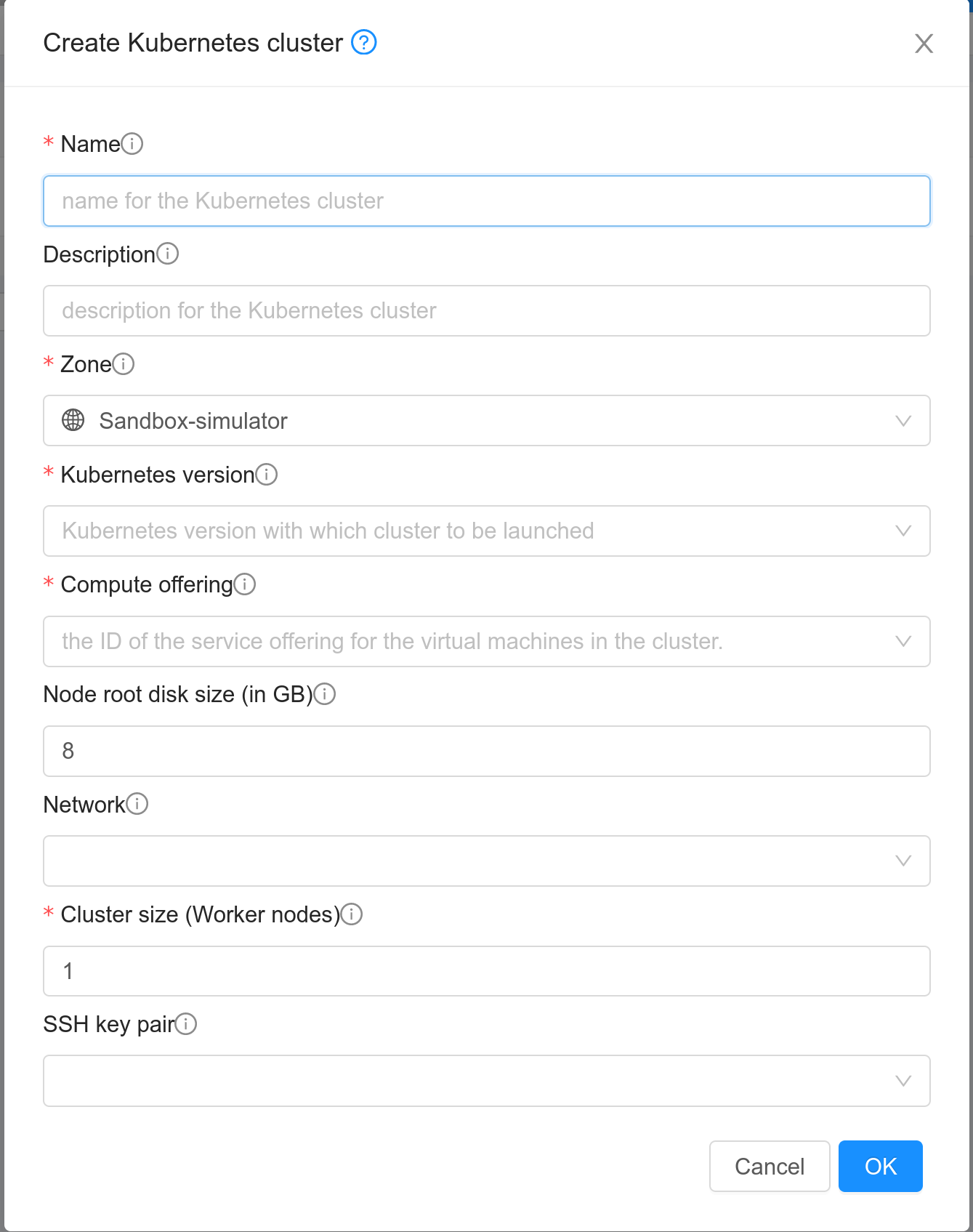
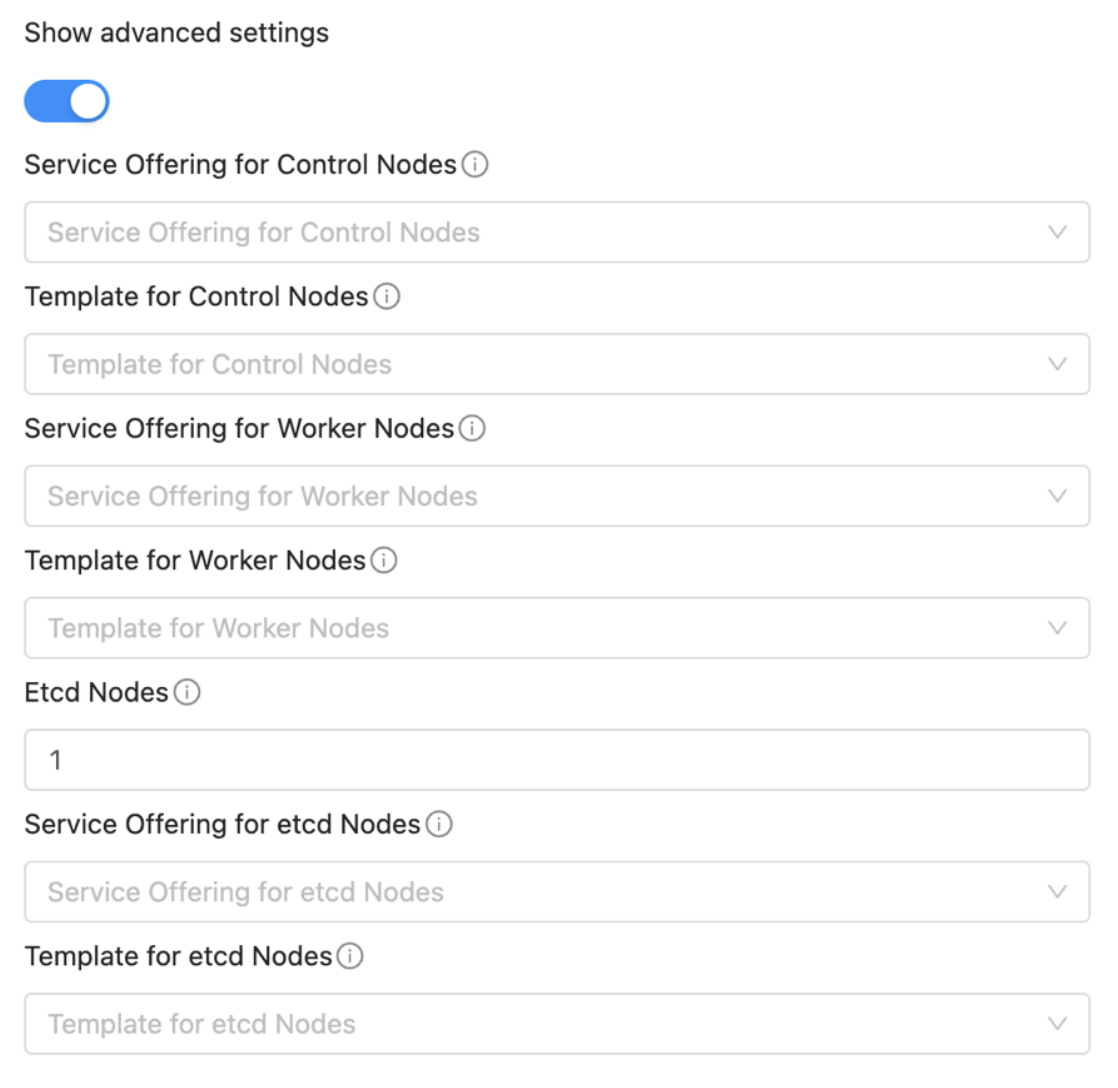
From 4.21.0, you can select the hypervisor type for Kubernetes cluster nodes. By default, no hypervisor is selected.
From 4.21.0, users will be provided with an optional section displayed on toggling the ‘Show Advanced Settings’ button. In this section, users can select templates and service offerings for: - Worker nodes - Control nodes - Etcd nodes (if etcd node count >= 1; By default etcd node count is 0)
For more information about the Advanced Settings see Flexible Kubernetes Clusters.
createKubernetesCluster API can be used to create new Kubernetes cluster. It takes following parameters as input,
name (name for the Kubernetes cluster; Required)
description (description for the Kubernetes cluster)
zoneid (availability zone in which Kubernetes cluster to be launched; Required)
clustertype (Define the type of cluster: CloudManaged (managed by CloudStack), ExternalManaged (managed by an external kubernetes provider). Defaults to CloudManaged)
kubernetesversionid (Kubernetes version with which cluster to be launched; Required for CloudManaged clusters)
serviceofferingid (the ID of the service offering for the Instances in the cluster; Required for CloudManaged clusters)
account (an optional Account for the Instance. Must be used with domainId)
domainid (an optional domainId for the Instance. If the account parameter is used, domainId must also be used)
projectid (Deploy cluster for the project)
networkid (Network in which Kubernetes cluster is to be launched)
keypair (name of the ssh key pair used to login to the Instances)
controlnodes (number of Kubernetes cluster control nodes, default is 1)
externalloadbalanceripaddress (external load balancer IP address while using shared Network with Kubernetes HA cluster)
size (number of Kubernetes cluster worker nodes; Required for manage clusters)
noderootdisksize (root disk size of root disk for each node)
dockerregistryusername (username for the docker image private registry; Experimental)
dockerregistrypassword (password for the docker image private registry; Experimental)
dockerregistryurl (URL for the docker image private registry; Experimental)
dockerregistryemail (email of the docker image private registry user; Experimental)
hypervisor (an optional parameter to specify the hypervisor on which the Kubernetes cluster will be deployed)
nodeofferings (an optional map parameter to set the service offerings for worker, control or etcd nodes. If this parameter is not set, then every VM in the cluster will be deployed using the default service offering set on the serviceofferingid parameter)
etcdnodes (An optional integer parameter that specifies the number of etcd nodes in the cluster. The default value is 0. If set to a value greater than 0, dedicated etcd nodes are created separately from the master nodes.)
nodetemplates: (an optional map parameter to set the template to be used by worker, control or etcd nodes. If not set, then every VM in the cluster will be deployed using the System VM template)
asnumber (an optional parameter to set the AS Number of the Kubernetes cluster network)
cniconfigurationid (an optional parameter to set the UUID of a registered CNI configuration)
cniconfigdetails (an optional parameter to specify the parameters values for the variables defined in the CNI configuration)
For example:
> create kubernetescluster name=Test description=Test-Cluster zoneid=34d23dd5-5ced-4e8b-9b0a-835a0b8ae2a6 size=1 noderootdisksize=10 serviceofferingid=a4f280a1-9122-40a8-8f0c-3adb91060f2a kubernetesversionid=6668e999-fe6c-4a91-88d8-d10bcf280d02
{
"kubernetescluster": {
"associatednetworkname": "Test-network",
"cpunumber": "4",
"description": "Test-Cluster",
"endpoint": "https://172.20.20.12:6443/",
"id": "74e3cc02-bbf7-438f-bfb0-9c193e90c1fb",
"kubernetesversionid": "6668e999-fe6c-4a91-88d8-d10bcf280d02",
"kubernetesversionname": "v1.13.2",
"controlnodes": 1,
"memory": "4096",
"name": "Test",
"networkid": "148af2cb-4b94-42a2-b701-3b6aa884cbb0",
"serviceofferingid": "a4f280a1-9122-40a8-8f0c-3adb91060f2a",
"serviceofferingname": "CKS Instance",
"size": 1,
"state": "Running",
"templateid": "17607ed6-1756-4ed7-b0f4-dbab5feff5b2",
"virtualmachineids": [
"da2cb67e-e852-4ecd-b16f-a8f16eb2c962",
"4179864a-88ad-4d6d-890c-c9b73c53589b"
],
"zoneid": "34d23dd5-5ced-4e8b-9b0a-835a0b8ae2a6",
"zonename": "KVM-advzone1"
}
}
On successful creation, the new cluster will automatically be started and will show up in Running state. If creation of the new cluster fails it can be in following states: - Alert – When node Instances were successfully provisioned, and cluster API server is accessible but further provisioning steps could not be completed. - Error – When the service was unable to provision the node Instances for the cluster or if the cluster API server is not accessible.
Note
A minimum of 2 cores of CPU and 2GB of RAM is needed for deployment. Therefore, the serviceofferingid parameter of createKubernetesCluster API must be provided with the ID of such compute offerings that conform to these requirements.
Private docker registry related parameters of createKubernetesCluster API (dockerregistryusername, dockerregistryusername, dockerregistryurl, dockerregistryemail) provides experimental functionality. To use them during cluster deployment value for global setting, cloud.kubernetes.cluster.experimental.features.enabled, must be set to true by admin beforehand.
Listing Kubernetes clusters
listKubernetesCluster API can be used to list existing Kubernetes clusters. id parameter can be passed as input to list details of a single supported version.
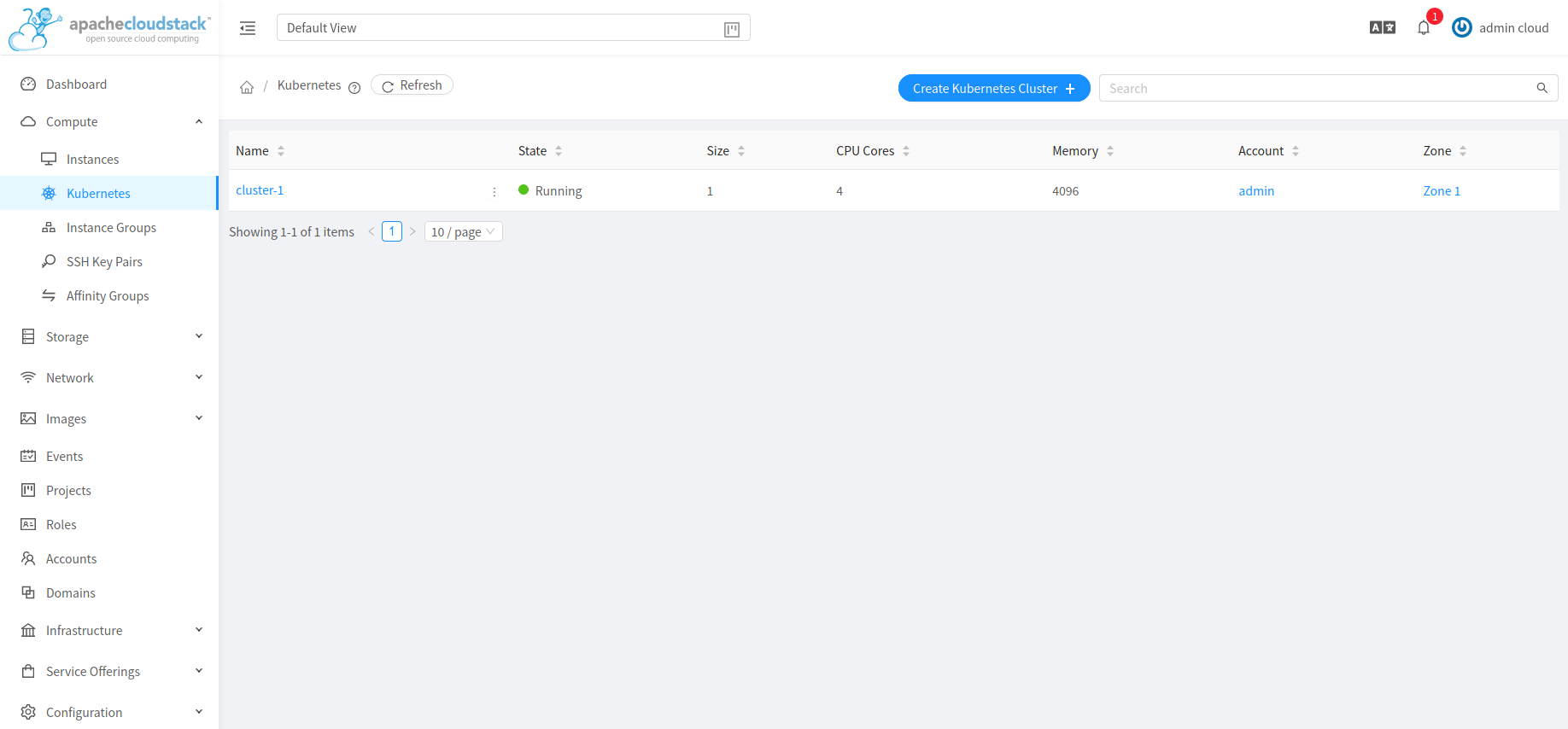
Stopping Kubernetes cluster
A running Kubernetes cluster can be stopped using either the stopKubernetesCluster API which takes id of the cluster as an input parameter or  action icon from UI. action icon is shown for a running cluster in the UI.
action icon from UI. action icon is shown for a running cluster in the UI.
Note
This operation is supported only for CloudManaged kubernetes cluster.
Starting a stopped Kubernetes cluster
A stopped Kubernetes cluster can be started using either the startKubernetesCluster API which takes id of the cluster as the input parameter or the  action icon from UI. action icon is shown for a stopped cluster in the UI.
action icon from UI. action icon is shown for a stopped cluster in the UI.
When the service fails to start a stopped cluster, the cluster will show in Alert state else it will show up as Running.
Note
This operation is supported only for CloudManaged kubernetes cluster.
Scaling Kubernetes cluster
A running or stopped Kubernetes cluster can be scaled using both API and UI.  action icon is shown for a running cluster in the UI which opens the form shown below,
action icon is shown for a running cluster in the UI which opens the form shown below,
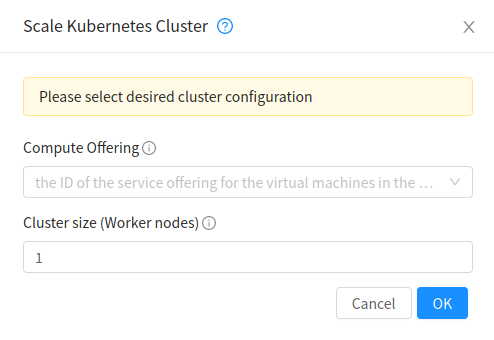
scaleKubernetesCluster API can be used to scale a running (or stopped cluster) to a desired cluster size and service offering. It takes the following parameters as input:
id (the ID of the Kubernetes cluster to be scaled; Required)
serviceofferingid (the ID of the new service offering for the Instances in the cluster)
size (number of Kubernetes cluster worker nodes)
Only running Kubernetes clusters can be scaled in size. When the service fails to scale the cluster, the cluster will show in Alert state else if the scaling is successful cluster will show up in Running state.
Note
Only up scaling is supported while scaling clusters for service offering.
This operation is supported only for CloudManaged kubernetes cluster
Upgrading Kubernetes cluster
A running Kubernetes cluster can be upgraded using both API and UI.  action icon is shown for a running cluster in the UI which opens the form shown below,
action icon is shown for a running cluster in the UI which opens the form shown below,
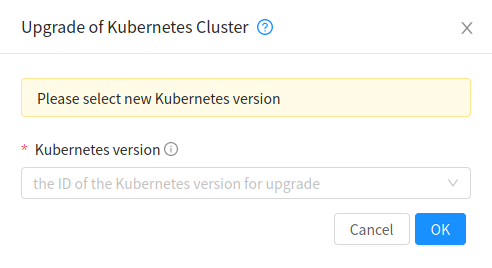
upgradeKubernetesCluster API can be used to upgrade a running cluster. It takes the following parameters as input:
id (the ID of the Kubernetes cluster to be upgraded; Required)
kubernetesversionid (Kubernetes version with which cluster to be launched; Required)
When the service fails to upgrade the cluster, the cluster will show up in Alert state, else if successful, the cluster appears Running state.
Note
Kubernetes can be upgraded from one MINOR version to the next MINOR version, or between PATCH versions of the same MINOR. That is, you cannot skip MINOR versions when you upgrade. For example, you can upgrade from 1.y to 1.y+1, but not from 1.y to 1.y+2. Therefore, service can upgrade running clusters in the similar manner only.
This operation is supported only for CloudManaged kubernetes cluster
Deleting Kubernetes cluster
A kubernetes cluster can be deleted using either the deleteKubernetesCluster API which takes cluster id as the input parameter or the  action icon from the UI.
action icon from the UI.
The Kubernetes service runs a background state scanner process which regularly checks the cluster health. For clusters in Alert state, this background process verifies their state and moves them to Running state if all node Instances of the cluster are running and the API server for the cluster is accessible.
Working with Kubernetes cluster
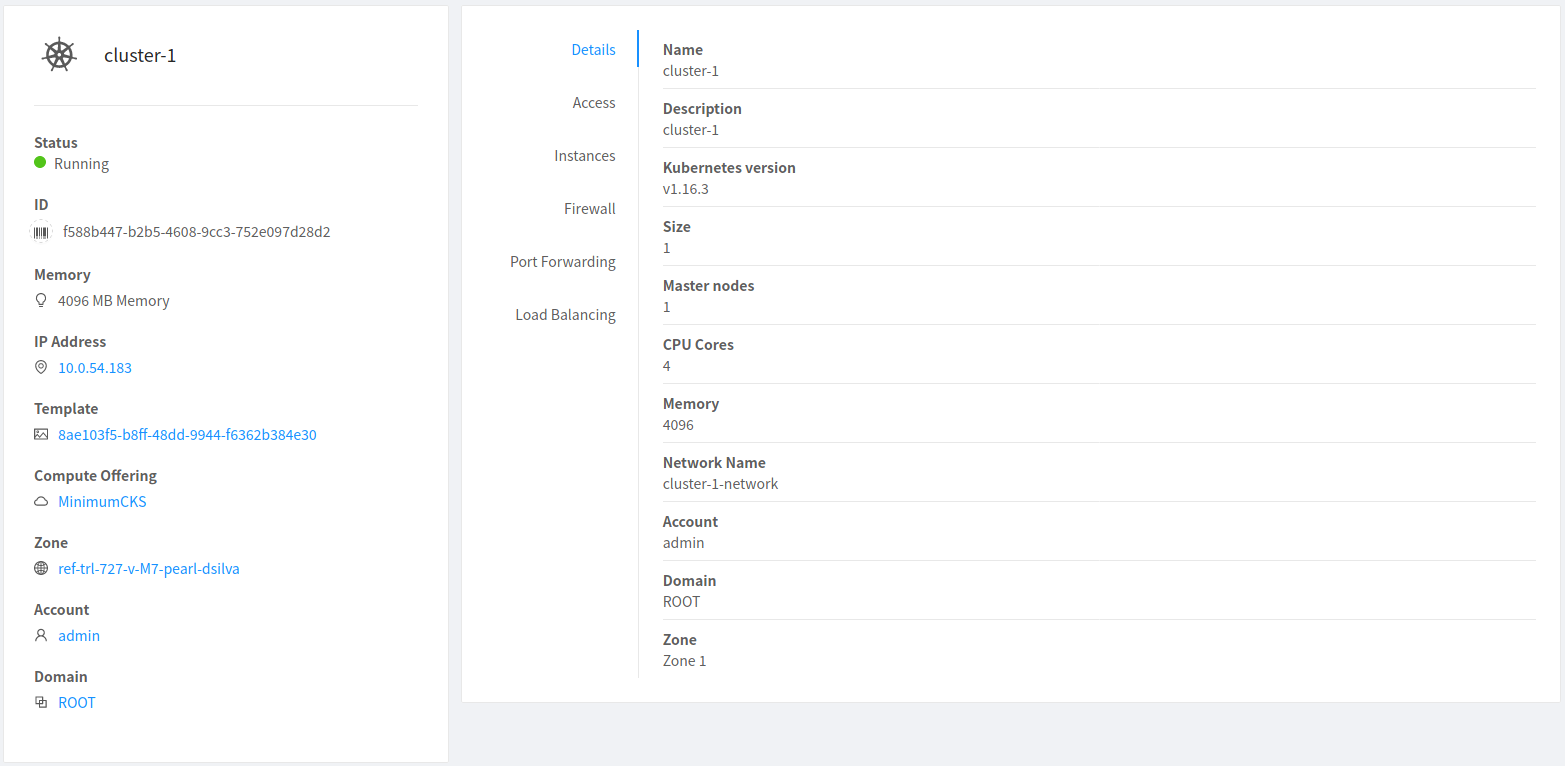
Once a Kubernetes cluster is created successfully and is in Running state, it can be accessed using the kubectl tool using the cluster’s kubeconfig file. The web dashboard can be accessed by running a local proxy using kubectl. Deployments in the cluster can be done using kubectl or web dashboard. More about deployment in Kubernetes here: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/deployment/
Accessing Kubernetes cluster
Instructions for accessing a running cluster will be shown in Access tab in the UI.
The service provides functionality to access kubeconfig file for a running Kubernetes cluster. This can be done using the UI or API. Action icon is shown in cluster detail UI to download kubeconfig file. UI will show download links for kubectl tool for different OS based on the cluster version.
getKubernetesClusterConfig API can be used to retrieve kubeconfig file data for a cluster. It takes id of the cluster as the input parameter.
Kubernetes cluster web dashboard
The service while creating a cluster automatically deploys dashboard for the cluster. More details about Kubernetes dashboard here: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/access-application-cluster/web-ui-dashboard/
Instructions for accessing the dashboard for a running cluster will be shown in the Access tab in the UI. Essentially, the user needs to run a local proxy first using kubectl and kubecofig file for the cluster to access the dashboard. For secure login, the service doesn’t enable kubeconfig based login for the dashboard. Token-based access is enabled and kubectl can be used to access service Account secret token.
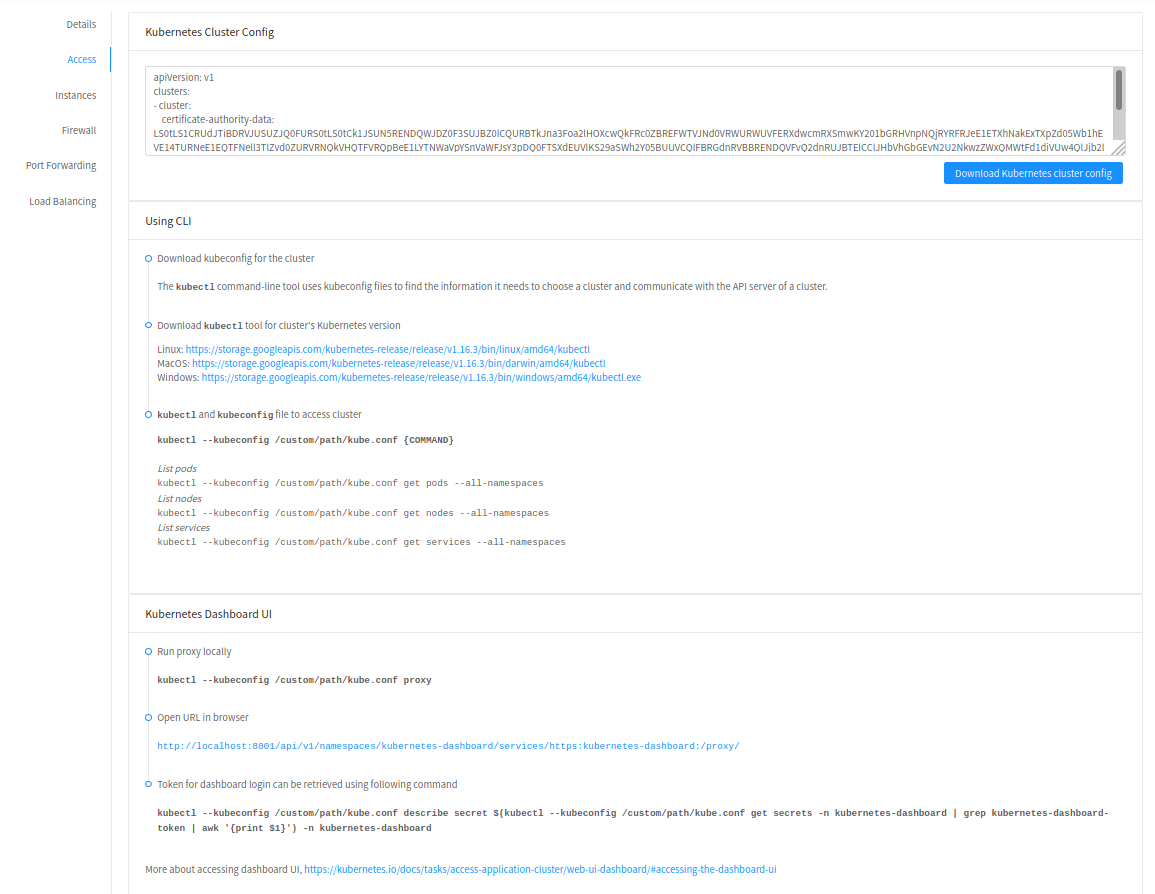
The following command can be used, while passing the correct path to kubeconfig file, to run proxy:
# kubectl --kubeconfig /custom/path/kube.config proxy
Once the proxy is running, users can open the following URL in the browser to access the dashboard,
http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/services/https:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/
Token for dashboard login can be retrieved using the following command:
# kubectl --kubeconfig /custom/path/kube.config describe secret $(kubectl --kubeconfig /custom/path/kube.config get secrets -n kubernetes-dashboard | grep kubernetes-dashboard-token | awk '{print $1}') -n kubernetes-dashboard
Kubernetes compatibility Matrix
ACS Version |
Supported Kubernetes Versions |
CKS Template |
SSH User |
|---|---|---|---|
4.14.x |
v1.11 onward (< 1.18) |
CoreOS |
core |
4.15.x |
v1.11 onward (< 1.18) |
CoreOS |
core |
4.16.0 |
v1.20 onward |
SystemVM Template (Debian) |
core |
4.16.1 |
v1.20 onward |
SystemVM Template (Debian) |
cloud |
Adding/Removing Instances for an ExternalManaged Kubernetes Cluster
The Instances launched by the external kubernetes provider can be linked to the ExternalManaged kubernetes cluster.
To add an Instance to an ExternalManaged Kubernetes cluster:
cmk add VirtualMachinesToKubernetesCluster id=59028a81-d9c9-46f6-bd16-8da918571c23 virtualmachineids=1d991764-3be8-4d2e-a9f1-2de2fc80ca72,97172931-286b-46c5-9427-ffc19315479e
To remove an Instance from an ExternalManaged Kubernetes cluster:
cmk remove VirtualMachinesFromKubernetesCluster id=59028a81-d9c9-46f6-bd16-8da918571c23 virtualmachineids=1d991764-3be8-4d2e-a9f1-2de2fc80ca72,97172931-286b-46c5-9427-ffc19315479e
Note
These operations are only supported for an ExternalManaged Kubernetes Cluster
Flexible Kubernetes Clusters
From 4.21.0, many enhancements have been added to CloudStack Kubernetes Service that allows users to:
Select the Hypervisor type for the Kubernetes Cluster nodes
Specify different templates and/or service offerings for different types of Kubernetes Clusters nodes
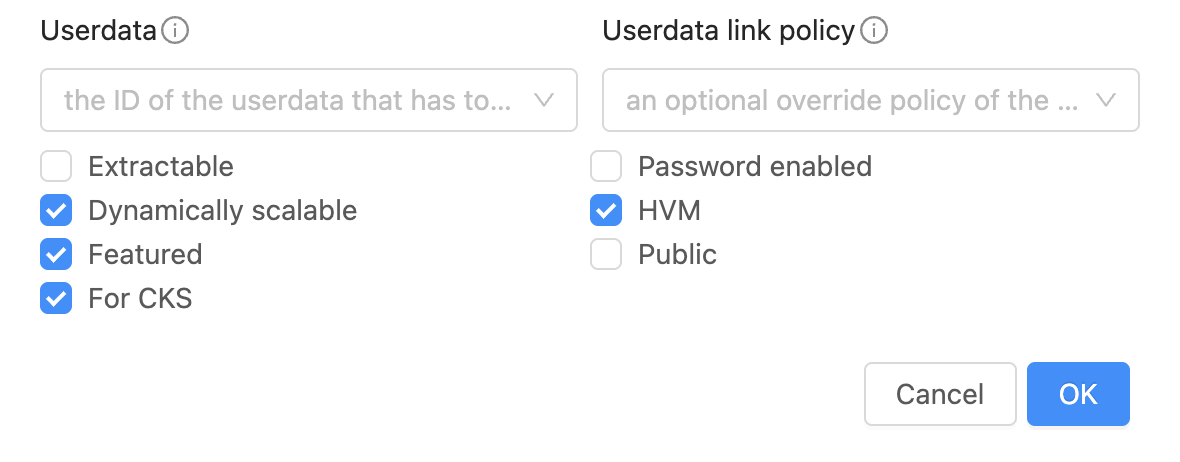
Use CKS-ready custom templates for Kubernetes cluster nodes marked as ‘For CKS’
Separate etcd nodes from control nodes of the Kubernetes clusters
Add and remove a pre-created instance as a worker node to an existing Kubernetes cluster
Mark Kubernetes cluster nodes for manual-only upgrade
Dedicate specific hosts/clusters to a specific domain for CKS cluster deployment
Use diverse CNI plugins (Calico, Cilium, etc)
Build a custom template to use for Kubernetes clusters nodes
CloudStack provides a custom CKS-ready template based on Ubuntu 22.04 to be used for Kubernetes clusters nodes: https://download.cloudstack.org/testing/custom_templates/ubuntu/22.04/.
This template contains all the required packages to be used as a Kubernetes cluster node. The default login credentials are: cloud:cloud.
A user may decide not to use the provided CKS-ready template and build their own template. The following needs to be made sure is present on the template:
The following packages or the equivalent ones for the specific OS need to be installed:
cloud-init cloud-guest-utils conntrack apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg gnupg-agent software-properties-common gnupg lsb-release python3-json-pointer python3-jsonschema containerd.io
A user named cloud needs to be created and added to the sudoers list:
sudo useradd -m -s /bin/bash cloud echo "cloud:<password>" | sudo chpasswd # Edit /etc/sudoers file with: cloud ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
Create the necessary directory /opt/bin:
sudo mkdir -p /opt/bin
Once the VM is deployed, place the Management Server’s SSH Public key at the cloud user’s authorized_keys file at ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Registering a custom template for Kubernetes cluster nodes
By default, the Kubernetes clusters nodes are deployed from the System VM template. On the Advanced Settings for Kubernetes clusters creation, CloudStack allows selecting templates for different types of nodes.
To register a template that will be listed as an option for Kubernetes cluster nodes:
Set URL to the provided CKS-ready template at: https://download.cloudstack.org/testing/custom_templates/ubuntu/22.04/ or a custom template built from the section above.
Set the template specific values as usual for template registration.
Mark the option ‘For CKS’. This ensures the template is considered as an option for Kubernetes cluster nodes on the Advanced Settings section for clusters creation.
Separate etcd nodes from control nodes
By default, a CKS cluster has 0 dedicated etcd nodes, and the etcd service runs on the control nodes. If etcd node count is set to a value greater than or equal to 1 during cluster creation, CloudStack will provision separate nodes exclusively for the etcd service, isolating them from the control nodes with the desired template and service offering if specified.
To use separate etcd nodes, it is required to build and register a CKS ISO version containing the etcd binaries as explained in: Kubernetes Supported Versions
For convenience, some CKS ISOs are uploaded to: https://download.cloudstack.org/testing/cks/custom_templates/iso-etcd/
Add an external VM Instance as a worker node to a Kubernetes cluster
Requirements for a VM Instance to be added as worker node to a Kubernetes cluster:
At least 8GB ROOT disk size, 2 CPU cores and 2GB RAM
The VM Instance must have a NIC on the Kubernetes cluster network
The Management Server’s SSH Public key must be added at the cloud user’s authorized_keys file at `~/.ssh/authorized_keys`.
The VM Instances meeting the requirements above can be added to the Kubernetes cluster by the addNodesToKubernetesCluster API specifying:
id (UUID of the Kubernetes cluster. Required)
nodeids (comma separated list of (external) node (physical or virtual machines) IDs that need to be added as worker nodes to an existing managed Kubernetes cluster (CKS). Required)
mountcksisoonvr (optional parameter for Vmware only, uses the CKS cluster network VR to mount the CKS ISO)
manualupgrade (optional parameter that indicates if the node is marked for manual upgrade and excluded from the Kubernetes cluster upgrade operation)
Note
Users will have the ability to add nodes to the Kubernetes cluster and mark them for manual upgrade. Once the nodes are marked for manual upgrade, the future cluster upgrade operations will exclude these nodes i.e., the Kubernetes version won’t be upgraded.
The following course of actions are taken:
Validation: The external node(s) are validated to ensure that all the above-mentioned prerequisites are present
Addition of port-forwarding rules and firewall rules (for isolated networks)
VM is rebooted with the Kubernetes configuration passed as user data
The ISO is attached either to the node or to the VR based on the value of mountcksisoonvr that is passed as a parameter to the addNodesToKubernetesCluster API (Vmware only).
The cluster enters Importing state until all the nodes are successfully added, and the number of Ready nodes is equal to the expected number of nodes to be added.
The process timeout is set by the setting: cloud.kubernetes.cluster.add.node.timeout.
Removing an external worker node from a Kubernetes cluster
External worker nodes can be removed from a Kubernetes cluster by the removeNodesFromKubernetesCluster API specifying:
id (UUID of the Kubernetes cluster. Required)
nodeids (comma separated list of (external) node (physical or virtual machines) IDs that need to be removed from an existing managed Kubernetes cluster (CKS). Required)
When node(s) are being removed from a Kubernetes cluster, the following happens:
On the control node, drain the specific node before it can be removed
Reset the corresponding worker node
Delete the worker node from the cluster on the control node
Remove the port-forwarding and firewall rules (for isolated networks) for the nodes being removed
The cluster enters RemovingNodes state until all the nodes are successfully removed, and the number of Ready nodes is equal to the expected number of nodes
The process timeout is set by the setting: cloud.kubernetes.cluster.remove.node.timeout.
Dedicate specific hosts/clusters to a specific domain for CKS cluster deployment
Administrators are able to dedicate hosts to a domain or account. CloudStack will take the host dedication into consideration when deploying Kubernetes clusters.
When there are no hosts dedicated to the domain/account the user belongs, then the nodes will be deployed on any host.
When there are hosts dedicated to the domain/account the user belongs, then the nodes will be deployed on the dedicated hosts.
Note
By design the hosts dedication does not consider the deployment of system VMs on the dedicated hosts (SSVM, CPVM and Virtual Routers). In case the Kubernetes cluster is created on an unimplemented network then the Virtual Router of the network will not be deployed on the dedicated hosts.
Use diverse CNI plugins (Calico, Cilium, etc)
A CNI framework has also been added which provides end users the flexibility to use the CNI plugin of their choice. The CNI framework internally leverages the managed User data feature provided by CloudStack.
Sample Calico CNI configuration data used which is appended to the existing Kubernetes control node user data is:
#cloud-config
- for i in {1..3}; do curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/calico/v3.28.0/manifests/calico.yaml -o /home/cloud/calico.yaml && break || sleep 5; done
- until [ -f /home/cloud/success ]; do sleep 5; done
- echo "Kubectl apply file"
- for i in {1..3}; do sudo /opt/bin/kubectl create -f /home/cloud/calico.yaml && break || sleep 5; done
- export PATH=$PATH:/home/cloud
- |
cat << 'EOF' > /home/cloud/create-configs.sh
#!/bin/bash
cat << 'EOL' > /home/cloud/bgp-config.yaml
apiVersion: crd.projectcalico.org/v1
kind: BGPConfiguration
metadata:
name: default
spec:
logSeverityScreen: Debug
asNumber: {{ AS_NUMBER }}
EOL
cat << 'EOL' > /home/cloud/bgp-peer.yaml
apiVersion: crd.projectcalico.org/v1
kind: BGPPeer
metadata:
name: bgp-peer-example
spec:
peerIP: {{ ds.meta_data.peer_ip_address }}
asNumber: {{ ds.meta_data.peer_as_number }}
EOL
EOF
- chmod +x /home/cloud/create-configs.sh
- /home/cloud/create-configs.sh
- for i in {1..3}; do sudo /opt/bin/kubectl apply -f /home/cloud/bgp-config.yaml && break || sleep 5; done
- for i in {1..3}; do sudo /opt/bin/kubectl apply -f /home/cloud/bgp-peer.yaml && break || sleep 5; done
The CNI Configuration creation allows specifying the parameters to be set as a comma separated list:
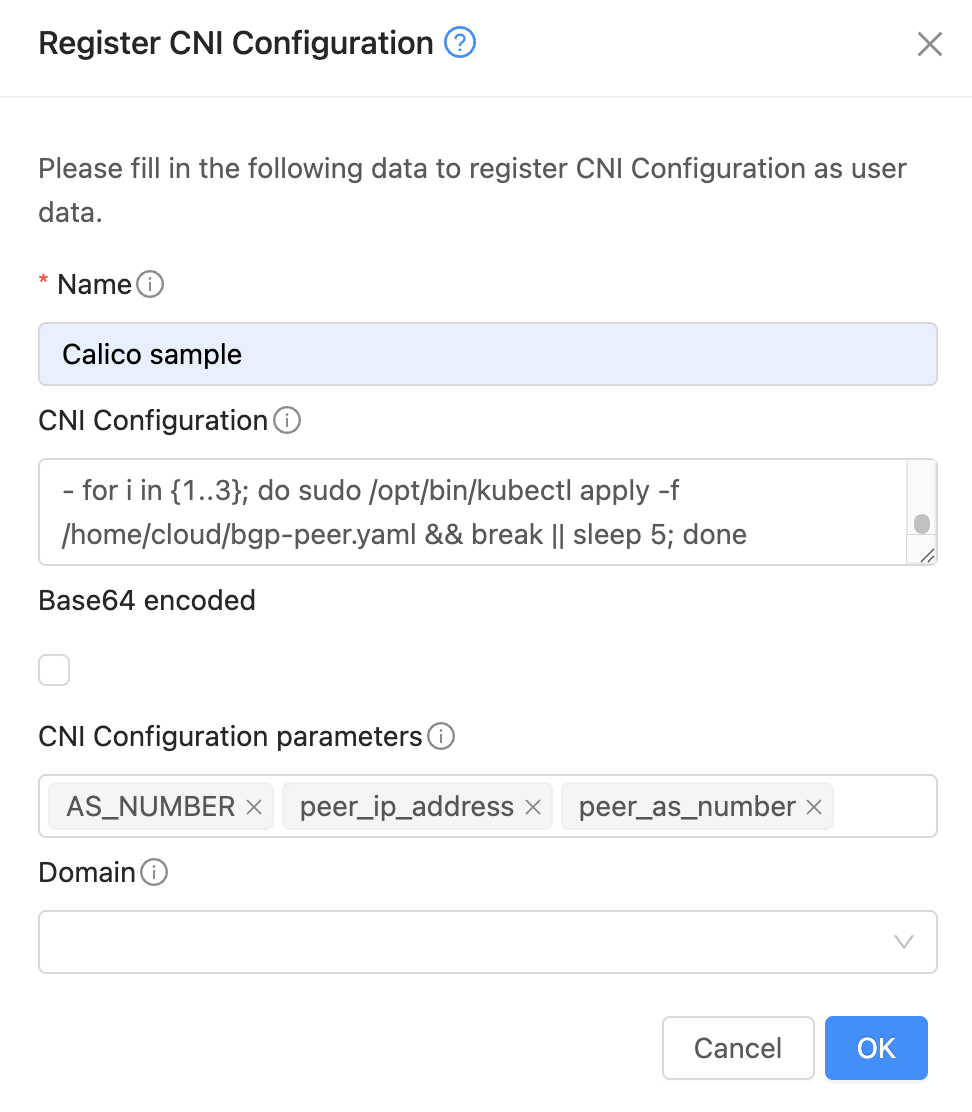
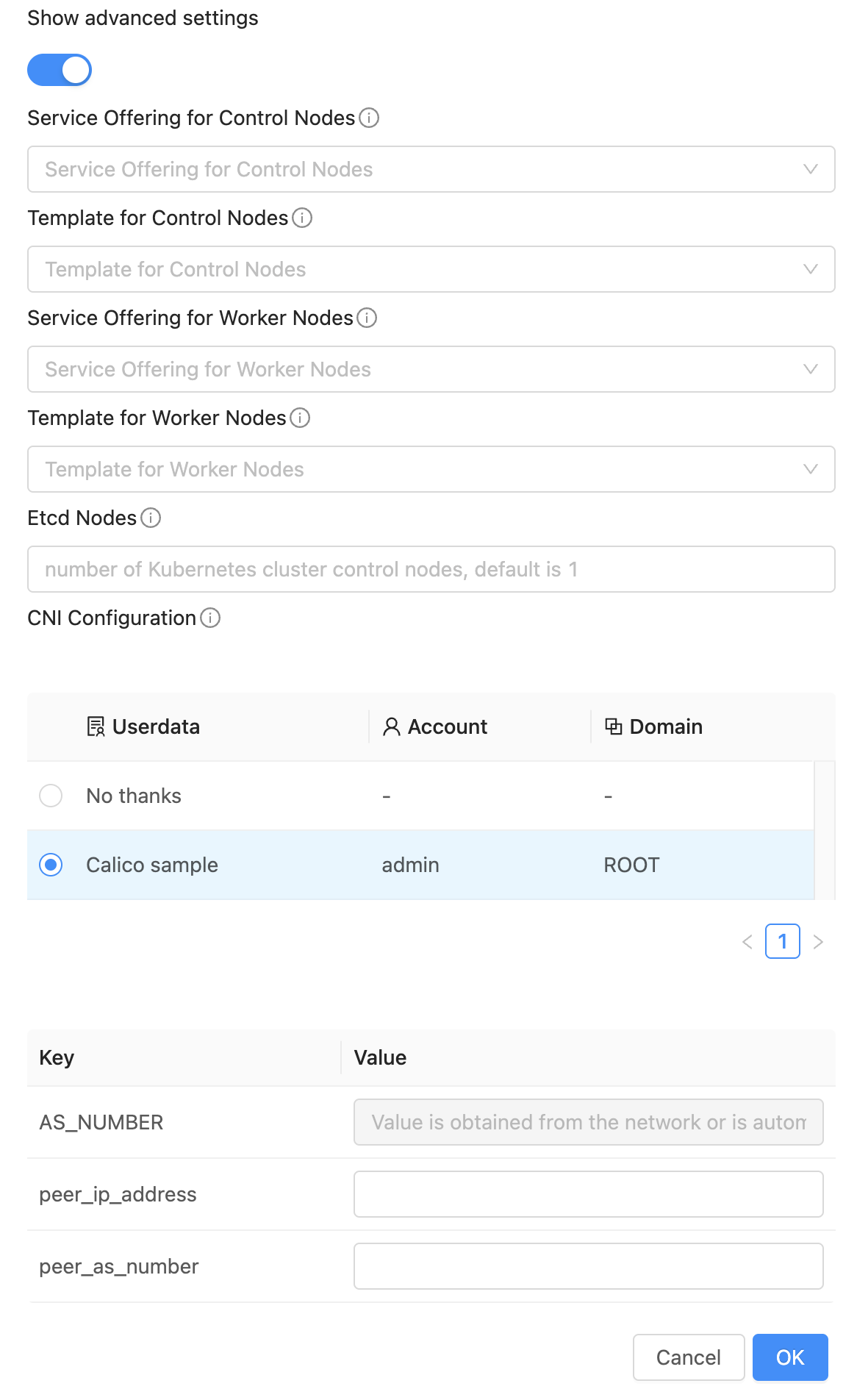
After a CNI Configuration is created, it can be appended to Kubernetes cluster nodes as part of ‘Advanced Settings’:
For verification of the applied CNI Configuration, the following commands can be used:
root@cksclusteradditon-control-190ca0ce253:~# kubectl get pods -A
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system calico-kube-controllers-8d76c5f9b-pkhcv 1/1 Running 6 (44m ago) 2d21h
kube-system calico-node-n4msg 1/1 Running 0 2d21h
kube-system calico-node-pdz2w 1/1 Running 0 2d18h
kube-system calico-node-slmg2 1/1 Running 0 2d21h
root@cksclusteradditon-control-190ca0ce253:~# kubectl get bgppeer
NAME AGE
bgp-peer-1 2d22h
root@cksclusteradditon-control-190ca0ce253:~# kubectl get bgpconfiguration
NAME AGE
default 2d22h
root@cksclusteradditon-control-190ca0ce253:~# kubectl describe bgpconfiguration
Name: default
Namespace:
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
API Version: crd.projectcalico.org/v1
Kind: BGPConfiguration
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2024-07-19T08:25:14Z
Generation: 1
Resource Version: 580
UID: 2b927b4e-82d3-4200-a3c1-9bf0cd5f5824
Spec:
As Number: 65145
Log Severity Screen: Debug
Events: <none>