Tuning
This section provides tips on how to improve the performance of your cloud.
Performance Monitoring
Host and guest performance monitoring is available to end users and administrators. This allows the user to monitor their utilization of resources and determine when it is appropriate to choose a more powerful service offering or larger disk.
Increase Management Server Maximum Memory
If the Management Server is subject to high demand, the default maximum JVM memory allocation can be insufficient. To increase the memory:
Edit the cloudstack-management.service configuration file at:
/etc/default/cloudstack-management
Change the command-line parameter from -XmxVVV to replace the VVV with an higher value.
For example, if the current is the default value is -Xmx2G, change it to -Xmx12G or another applicable value. Make sure not to go over about 2/3rd of the actual physical memory of the machine.
To put the new setting into effect, restart the Management Server.
# systemctl restart cloudstack-management
For more information about memory issues, see “FAQ: Memory” at Tomcat Wiki.
Set Database Buffer Pool Size
It is important to provide enough memory space for the MySQL database to cache data and indexes:
Edit the MySQL configuration file:
/etc/my.cnf
Insert the following line in the [mysqld] section, below the datadir line. Use a value that is appropriate for your situation. We recommend setting the buffer pool at 40% of RAM if MySQL is on the same server as the management server or 70% of RAM if MySQL has a dedicated server. The following example assumes a dedicated server with 1024M of RAM.
innodb_buffer_pool_size=700M
Restart the MySQL service.
# service mysqld restart
For more information about the buffer pool, see “The InnoDB Buffer Pool” at MySQL Reference Manual.
Monitor the Database Load
The load of the database is monitored. By default the queries for each minute are calculated in queries per second. Three values are retaint by default. In the UI these are visible under the DB/Usage Server page under the infrastructure menu.
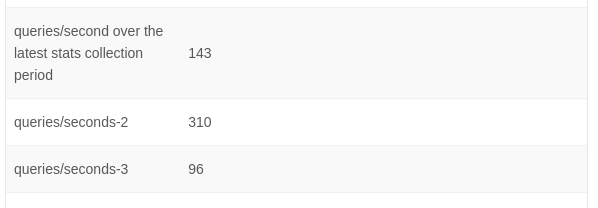
The configuration variable ‘database.server.stats.interval’ can be set to change the interval, which is 60 seconds by default.
The value of ‘database.server.stats.retention’ can be changed to tweak the number of values that are maintained.
Set and Monitor Total Instance Limits per Host
The CloudStack administrator should monitor the total number of Instances in each cluster and disable allocation to the cluster if the total is approaching the maximum that the hypervisor can handle. Be sure to leave a safety margin to allow for the possibility of one or more hosts failing, which would increase the Instance load on the other hosts as the Instances are automatically redeployed. Consult the documentation for your chosen hypervisor to find the maximum permitted number of Instances per host, then use CloudStack global configuration settings to set this as the default limit. Monitor the Instance activity in each cluster at all times. Keep the total number of Instances below a safe level that allows for the occasional host failure. For example, if there are N hosts in the cluster, and you want to allow for one host in the cluster to be down at any given time, the total number of Instances you can permit in the cluster is at most (N-1) * (per-host-limit). Once a cluster reaches this number of Instances, use the CloudStack UI to disable allocation of more Instances to the cluster.
Configure XenServer dom0 Memory
Configure the XenServer dom0 settings to allocate more memory to dom0. This can enable XenServer to handle larger numbers of Instances. We recommend 2940 MB of RAM for XenServer dom0. For instructions on how to do this, see Citrix Knowledgebase Article.The article refers to XenServer 5.6, but the same information applies to XenServer 6
Purging Expunged Resources
Note
Currently only available for Instances and their linked resources.
Over the time there are chances of piling up of millions of database records for the removed or expunged resources. The presence of a lot of useless records in the database can also affect the performance of the cloud so it is needed to purge such entries in a systematic way. CloudStack provides the following methods to allow purging of the expunged resources and their database records:
Using background task
A background task will run at regular intervals. The interval for the task and other parameters for it such as resource types, start and end date and batch size can also be controlled with the help of global settings.
The following new global settings have been introduced which would allow configuring background task for purging the expunged resources:
Global setting |
Default values |
Description |
|---|---|---|
expunged.resources.purge.enabled |
false |
Whether to run a background task to purge the DB records of the expunged resources. |
expunged.resources.purge.resources |
(empty) |
A comma-separated list of resource types that will be considered by the background task to purge the DB records of the expunged resources. Currently only VirtualMachine is supported. An empty value will result in considering all resource types for purging. |
expunged.resources.purge.interval |
86400 |
Interval (in seconds) for the background task to purge the DB records of the expunged resources. |
expunged.resources.purge.delay |
300 |
Initial delay (in seconds) to start the background task to purge the DB records of the expunged resources task. |
expunged.resources.purge.batch.size |
50 |
Batch size to be used during purging of the DB records of the expunged resources. |
expunged.resources.purge.start.time |
(empty) |
Start time to be used by the background task to purge the DB records of the expunged resources. Use format yyyy-MM-dd or yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss. |
expunged.resources.purge.keep.past.days |
30 |
The number of days in the past from the execution time of the background task to purge the DB records of the expunged resources for which the expunged resources must not be purged. To enable purging DB records of the expunged resource till the execution of the background task, set the value to zero. |
Using API
An admin-only API purgeExpungedResources allows purging the expunged resources with desired parameters. It will allow passing the following parameters - resourcetype, batchsize, startdate, enddate. An example of purgeExpungedResources API call is shown below:
> purge expungedresources startdate=2024-04-15 enddate=2024-04-20 resourcetype=VirtualMachine
{
"purgeexpungedresourcesresponse": {
"resourcecount": 6
}
}
Using configuration in offerings
- ..note::
Available only for service offerings
_purgeresources_ configuration for offerings can be used to allow immediately purging a resource when it is expunged. The configuration can be set to true or false _purgeresources_ parameter while creating the corresponding offerings. The following global setting can be used to control the delay for purging the resource after expunge:
Global setting |
Default values |
Description |
|---|---|---|
expunged.resource.purge.job.delay |
180 |
Delay (in seconds) to execute the purging of the DB records of an expunged resource initiated by the configuration in the offering. Minimum value should be 180 seconds and if a lower value is set then the minimum value will be used. |