About Elastic IPs
Elastic IP (EIP) addresses are the IP addresses that are associated with an account, and act as static IP addresses. The account owner has the complete control over the Elastic IP addresses that belong to the account. As an account owner, you can allocate an Elastic IP to a VM of your choice from the EIP pool of your account. Later if required you can reassign the IP address to a different VM. This feature is extremely helpful during VM failure. Instead of replacing the VM which is down, the IP address can be reassigned to a new VM in your account.
Similar to the public IP address, Elastic IP addresses are mapped to their associated private IP addresses by using StaticNAT. The EIP service is equipped with StaticNAT (1:1) service in an EIP-enabled basic zone. The default network offering, DefaultSharedNetscalerEIPandELBNetworkOffering, provides your network with EIP and ELB network services if a NetScaler device is deployed in your zone. Consider the following illustration for more details.
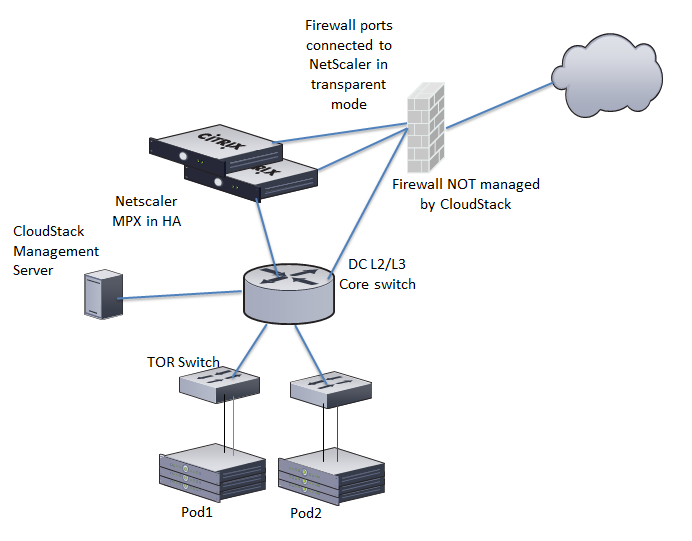
In the illustration, a NetScaler appliance is the default entry or exit point for the CloudStack instances, and firewall is the default entry or exit point for the rest of the data center. Netscaler provides LB services and staticNAT service to the guest networks. The guest traffic in the pods and the Management Server are on different subnets / VLANs. The policy-based routing in the data center core switch sends the public traffic through the NetScaler, whereas the rest of the data center goes through the firewall.
The EIP work flow is as follows:
When a user VM is deployed, a public IP is automatically acquired from the pool of public IPs configured in the zone. This IP is owned by the VM’s account.
Each VM will have its own private IP. When the user VM starts, Static NAT is provisioned on the NetScaler device by using the Inbound Network Address Translation (INAT) and Reverse NAT (RNAT) rules between the public IP and the private IP.
Note
Inbound NAT (INAT) is a type of NAT supported by NetScaler, in which the destination IP address is replaced in the packets from the public network, such as the Internet, with the private IP address of a VM in the private network. Reverse NAT (RNAT) is a type of NAT supported by NetScaler, in which the source IP address is replaced in the packets generated by a VM in the private network with the public IP address.
This default public IP will be released in two cases:
When the VM is stopped. When the VM starts, it again receives a new public IP, not necessarily the same one allocated initially, from the pool of Public IPs.
The user acquires a public IP (Elastic IP). This public IP is associated with the account, but will not be mapped to any private IP. However, the user can enable Static NAT to associate this IP to the private IP of a VM in the account. The Static NAT rule for the public IP can be disabled at any time. When Static NAT is disabled, a new public IP is allocated from the pool, which is not necessarily be the same one allocated initially.
For the deployments where public IPs are limited resources, you have the flexibility to choose not to allocate a public IP by default. You can use the Associate Public IP option to turn on or off the automatic public IP assignment in the EIP-enabled Basic zones. If you turn off the automatic public IP assignment while creating a network offering, only a private IP is assigned to a VM when the VM is deployed with that network offering. Later, the user can acquire an IP for the VM and enable static NAT.
For more information on the Associate Public IP option, see “Creating a New Network Offering”.
Note
The Associate Public IP feature is designed only for use with user VMs. The System VMs continue to get both public IP and private by default, irrespective of the network offering configuration.
New deployments which use the default shared network offering with EIP and ELB services to create a shared network in the Basic zone will continue allocating public IPs to each user VM.